In this Guest Post, the UK’s ‘Classical Seat’ trainer Heather Moffett looks at how the rider’s seat can make movement harder for the horse. It’s something that saddle fitters know about, but it’s often the last thing riders think of: the riding position as much as the saddle fit affects their horse’s back and movement.
Heather Moffett has over 40 years’ instruction experience. Chiefly following the French school of classical equitation, which focuses on dressage as an art form rather than competition, she is best known as an authority on the Classical Seat. Recently, she launched The Online Riding School, a library of videos suitable for everyone from complete beginners to advanced riders – visit now to benefit from the introductory offers.
We all keep hearing about ‘connection’. It’s a current buzzword and usually means connecting with your horse on the ground, either through loose or in-hand work.
Many riders assume this will enable them to achieve the same connection once mounted.
There is nothing wrong with that. However, they often then wonder why they lose that connection – sometimes literally, complete with the saddle(!) – once they start riding. The fact is that they are, in ignorant bliss, impeding the horse!
The Disconnected Seat
 If the rider is out of sync with the horse’s movement, the flow and harmony will always be disrupted as the horse struggles to balance the rider as well as himself.
If the rider is out of sync with the horse’s movement, the flow and harmony will always be disrupted as the horse struggles to balance the rider as well as himself.
Or, he endures the discomfort of a rider sitting like a lump of lead, driving with the seat against his sensitive back, or bouncing stiffly in the saddle.
The horse has only one way to show his discomfort or pain, as he is mute, and that is by behaviour that is then construed as ‘misbehaviour’.
I often ask riders who kick and hit their horses if they would do the same to their dog. The dog is able to cry out in pain. The horse cannot, and it is his muteness, throughout history, that has led to his downfall and still does to this day.
What Gets My Goat is This
I’ve been a specialist trainer/teacher of the Classical seat for 46 years. In that time, there has been little interest in increasing knowledge of the seat and refinement of the aids.
So many teachers and trainers say that it is necessary to ignore imperfections in the seat until “the horse is going well”. Then they wonder why the horse never progresses, or why force must be resorted to, in order to make the horse submit!
Yes, there is that word submit (or submission) that’s a requirement in a dressage test.
My own teachers soon found that it worked far better to encourage my cooperation in school rather than forcing me into submission! And a horse is no different.
I would like to see the word submission in tests replaced with willing cooperation.
How different would the expression be on many a horse’s face, if he were trained as a partner, and not as an adversary?
So, are you screwing up your horse with your seat, without even noticing? Here are the 5 top points I’d like you to think about.
1. Saddle Fit Woes (Yes, Again)

No surprises for this one. Saddle fit is probably the most obvious thing that needs to be right, but many saddles are a long way from perfect. That’s true even in my home of the UK, where saddles are most often professionally fitted.
But, what amazes me is the number of saddles I see with clients coming to me for lessons that have faults that make it damn near impossible for the rider to sit either straight or in balance!
Here are the worst offenders.
The saddle is too narrow. This is still one of the most common faults – it pinches the horse and tips the rider’s pelvis backward, aiding a chair seat rather than the ear/shoulder/hip/heel line which is the only position of balance.
Try walking with your butt stuck out behind you and knees up, as though sitting on a chair! It’s hard enough to even remain upright! Your weight will be over the cantle region, making it difficult for the horse to lift and round his back, and causing him to go hollow.
Stirrup bars are, almost without exception, even on many dressage saddles, too far forwards. This is why the rider is constantly being nagged by instructors to “get that lower leg back”!
I do wonder why instructors and even top dressage trainers, never seem to notice that all of their students are not anatomically challenged and there might just be something wrong with the saddle design and balance!! (Don’t get me started!!)
2. An Insecure Seat Sucks (for Both Horse and Rider)

Here’s what I mean by insecure. Riders are not taught to absorb and sync with the horse’s movement.
We hear:
“Sit deeper!”
“Relax your back!”
“Go with the movement!”
“Follow the horse’s movement!”
Well, usually if you are following something you are behind it!
Is it any wonder beginners are confused and often never learn to move in sync with the horse?
If this describes you, fear not. I have had riders here on my horse movement simulator workshops who’ve been riding 10, 20 or more years, and still they have never learned to move in sync with the horse.
3. Saddle Seat Glue Hasn’t Been Invented Yet

If you’re bouncing around, or driving with both seat bones to achieve some adhesion to the saddle, or sitting on your back pockets and collapsing the rib cage, you will be making your horse’s life more difficult.
It is so NOT rocket science to learn this!
But until teachers are trained to teach it, the situation will not improve!!
And it is not just novice riders who block their horse through incorrect adhesion to the saddle.
Look at the nodding head, flailing legs (usually with spurs attached) riders to be seen even in the Grand Prix dressage arena…
4. Horses Have the Low Down on Our Weight Issues…
How many times do you hear it said that a horse can feel a fly land on his back? So how much more can he feel his rider, whether good or bad?
For me, my aim – both as a rider myself and also as a trainer – is to be as little burden on the back of my horse as possible.

I aim to do this by sitting lightly, but deeply, in sync with his movement.
If the rider is crooked, possibly due to a problem with the saddle, or is asymmetric due to their own physical problem, the horse suffers.
He has to cope with this and compensate, usually by going crookedly himself.
And there’s more. The use of the rider’s body as a primary aid, is so rarely taught. Yet when utilised, it is the most invisible aid of all. Combined with the seat bones moving in sync with the horse’s back, it is the secret to an elegant harmonious seat, that appears to be doing nothing.
That’s when the horse and rider glide through all the movements as though they are one being – like a Centaur.
5. ‘Feel’ Begins in your Backside (I Mean It!)
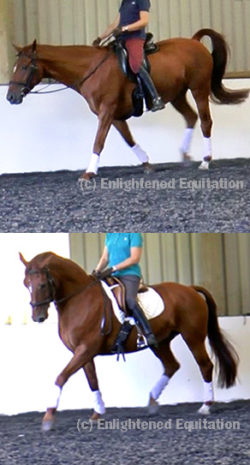
‘Connection’ means being able to feel, and not just when working from the ground. We all have nerve endings in our backsides – if you are taught what to feel and how to feel, it is within the grasp of any rider, even beginners.
And ‘aid’ really means ‘help’. If you learn to use aids that make biomechanical sense to the horse, they do become truly invisible as the horse becomes more and more sensitive with correct training.
BUT, if the horse hasn’t been schooled to respond to specific aids, then is it any wonder he is confused and ‘misbehaves’? It’s a bit like us lazy Brits here, shouting at foreigners in the hope they will understand English then getting annoyed when they don’t!
Your seat can genuinely aid (help) your horse. This happens when you’re taught not only the hand and leg aids, but also:
- the weight aids for turning,
- the seat aid for collecting and for downward transitions,
- the precise positioning of the torso in lateral work and circles/ bends, etc.
At this point, riding becomes a whole language, which almost all horses quickly understand. Why? Because it is working with, not against, their own body.
Moving in sync with the horse allows the rider to learn ‘feel’, that term that often seems to imply that only a favoured few have the ability to learn it.
Rubbish!
So, in closing, if you wish to have true connection with your horse, you need to:
a) Absolutely not screw up either his back or his brain,
b) Learn to ride to the best of your ability, and
c) Treat your horse as a partner and friend, and not as a tool merely to win the next rosette.
If winning happens as a by-product of good riding, even better, but if your horse is not progressing, look to your own riding and equipment before you blame your horse. Get these 5 points sorted and you’ll be well on your way to true connection with your horse!
Questions, thoughts or comments? Join us at The Horse’s Back Facebook Group.
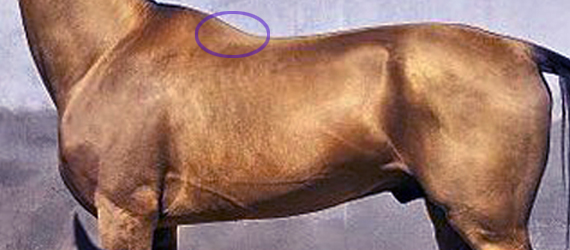
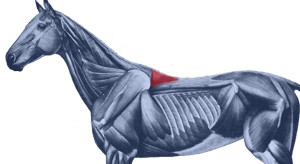 At best, it has no more than a bit part in anatomical illustrations, usually as a small triangular area at the base of the withers. This is also where we can palpate it.
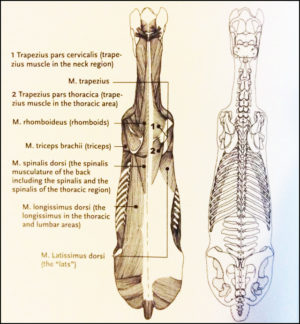
At best, it has no more than a bit part in anatomical illustrations, usually as a small triangular area at the base of the withers. This is also where we can palpate it.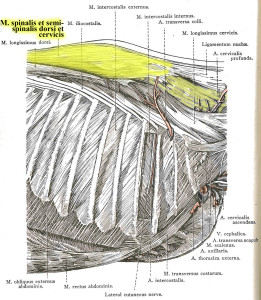 Further back along the spine, it lies medially to Longissimus dorsi, and in fact integrates with this larger, better known muscle, attaching to the processes of the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae.
Further back along the spine, it lies medially to Longissimus dorsi, and in fact integrates with this larger, better known muscle, attaching to the processes of the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae.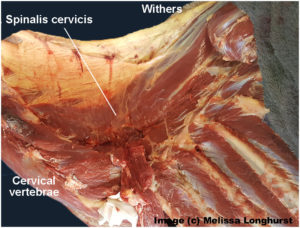 Its integration with other muscles is complex, and its close relationship with Longissimus dorsi partially explains why it doesn’t get much consideration as a muscle in its own right.
Its integration with other muscles is complex, and its close relationship with Longissimus dorsi partially explains why it doesn’t get much consideration as a muscle in its own right.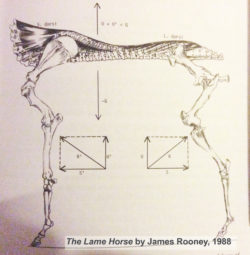 In his 1980s’ Guide to Lameness videos, Dr. James Rooney, first director of the Gluck Equine Research Center, University of Kentucky, referred to Spinalis as part of the suspension bridge of muscles supporting the spine (Longissimus dorsi achoring from the lumbosacral vertebrae, Spinalis thoracis et dorsalis from the upper thoracics). He also refers to this extensively in The Lame Horse (1988).
In his 1980s’ Guide to Lameness videos, Dr. James Rooney, first director of the Gluck Equine Research Center, University of Kentucky, referred to Spinalis as part of the suspension bridge of muscles supporting the spine (Longissimus dorsi achoring from the lumbosacral vertebrae, Spinalis thoracis et dorsalis from the upper thoracics). He also refers to this extensively in The Lame Horse (1988).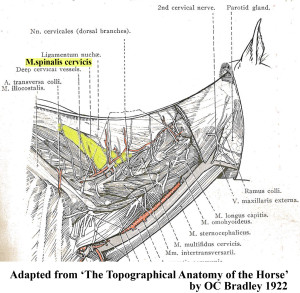
 What often happens is this. An overtight saddle fits over the base of the withers like a clothes peg, pinching Trapezius thoracis and Longissimus dorsi. However, it frequently misses Spinalis thoracis where it surfaces, wholly or partially within the gullet space. Often, the muscle is partially affected.
What often happens is this. An overtight saddle fits over the base of the withers like a clothes peg, pinching Trapezius thoracis and Longissimus dorsi. However, it frequently misses Spinalis thoracis where it surfaces, wholly or partially within the gullet space. Often, the muscle is partially affected.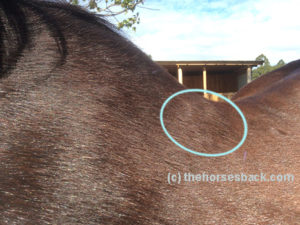
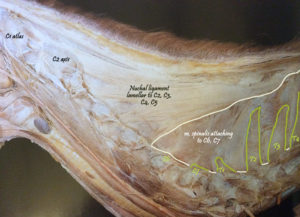
 The muscle is tinted green in this image from Sisson and Grossman’s The Anatomy of Domestic Animals, Volume 1, fifth edition 1975. Here, it is labelled Spinalis et semi-spinalis cervicis. This anatomical figure is credited to an earlier text, Ellenberger and Baum, 1908. (added 23 Dec 2016)
The muscle is tinted green in this image from Sisson and Grossman’s The Anatomy of Domestic Animals, Volume 1, fifth edition 1975. Here, it is labelled Spinalis et semi-spinalis cervicis. This anatomical figure is credited to an earlier text, Ellenberger and Baum, 1908. (added 23 Dec 2016)
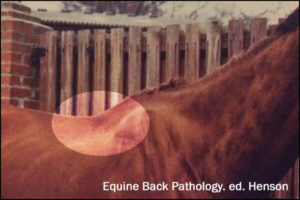
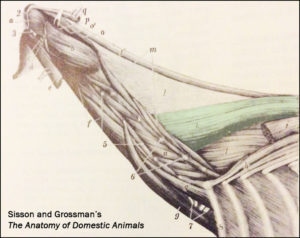
 Master Saddler Jochen Schleese refers to Spinalis dorsi and its function in stabilizing the withers in Suffering in Silence, his passionate book about saddle fitting from 2014. “This muscle area is especially prone to significant development – especially with jumpers – because it is continually contracted to accommodate the shock of landing”. The surface area of the muscle is indicated in the anatomical figure, reproduced here. (added 23 Dec 2016)
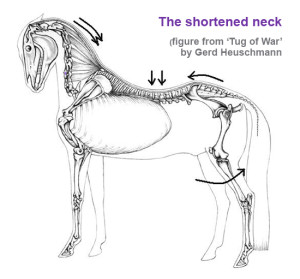
Master Saddler Jochen Schleese refers to Spinalis dorsi and its function in stabilizing the withers in Suffering in Silence, his passionate book about saddle fitting from 2014. “This muscle area is especially prone to significant development – especially with jumpers – because it is continually contracted to accommodate the shock of landing”. The surface area of the muscle is indicated in the anatomical figure, reproduced here. (added 23 Dec 2016) In his seminal text addressing issues of modern dressage training, Tug of War, 2007, Gerd Heuschmann includes Spinalis cervicis in the triangle formed by the rear of the rear of the cervical spine, the withers, and the shoulder blades, “… an extensive connection between the head-neck axis and the truck… it explains how the position and length of the horse’s neck directly affects the biomechanics of the back.” (added 31 Dec 2016)
In his seminal text addressing issues of modern dressage training, Tug of War, 2007, Gerd Heuschmann includes Spinalis cervicis in the triangle formed by the rear of the rear of the cervical spine, the withers, and the shoulder blades, “… an extensive connection between the head-neck axis and the truck… it explains how the position and length of the horse’s neck directly affects the biomechanics of the back.” (added 31 Dec 2016)